Heat Capacity
Heat Capacity: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Ratio of Specific Heats, Molar Specific Heat Capacity at Constant Volume, Relation Between Molar and Principal Specific Heat Capacities & Principal Specific Heat Capacity of a Gas at Constant Pressure etc.
Important Questions on Heat Capacity
For a gas of molecular weight specific heat capacity at constant pressure is
Why the specific heat at a constant pressure is more than that at constant volume.
What is specific heat of gas at constant pressure
At a given temperature, the specific heat of a gas at constant pressure is always greater than its specific heat at constant volume.
and are specific heats at constant pressure and constant volume respectively. It is observed that, for hydrogen gas and for nitrogen gas. The correct relation between and is:
Assertion: The specific heat at constant pressure is greater than the specific heat at constant volume i.e., .
Reason: In case of specific heat at constant volume, the whole of heat supplied is used to raise the temperature of one mole of the gas through while in case of specific of heat at constant pressure, heat is to be supplied not only for heating 1 mole of gas through but also for doing work during expansion of the gas.
An insulated box containing a diatomic gas of molar mass is moving with velocity . The box is suddenly stopped. The resulting change in temperature is . What will be the value of ?
If and denote the specific heats of nitrogen gas per unit mass at constant pressure and constant volume respectively, then
The ratio of the molar heat capacities of a diatomic gas at constant pressure to that at constant volume is
A molecule of a gas has six degrees of freedom. Then, the molar specific heat of the gas at constant volume is
One gram mole of an ideal gas with the ratio of constant pressure and constant volume specific heats is mixed with gram moles of another ideal gas with . If the for the mixture is , then what will be the value of ?
A rigid triangular molecule consists degrees of freedom. The adiabatic constant of an ideal gas consisting of such molecules is
Specific heat of an ideal gas at constant volume and at constant pressure are related to universal gas constant are as
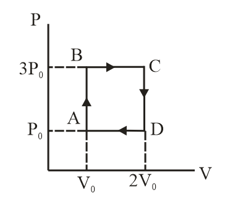
An ideal monatomic gas is carried along the cycle as shown in the figure. The total heat absorbed in this process is
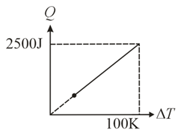
One mole of a gas mixture is heated under constant pressure, and heat supplied is plotted against temperature difference acquired. Find the approximate value of for mixture:
For the next three questions
An ideal diatomic gas is expanded so that the amount of heat transferred to the gas is equal to the decrease in its internal energy.
The molar specific heat of the gas in this process is given by C whose value is
Two mole of oxygen is mixed with eight mole of helium. The effective specific heat of the mixture at constant volume is _____.
Which of the following is correct for a gas with, and .
(Take, .)
Calculate the change of heat when of water at is heated to ? (specific heat of water )
It is known that the value of is for a mixture comprising of moles of a monoatomic gas and moles of a diatomic. Then identify the correct option.
